What is Microsoft Hyper-V ?
Hyper-V is a native hypervisor from Microsoft that allows users to create and manage virtual machines (VMs). It’s an integral part of Windows Server and provides a virtualized environment for running multiple operating systems on a single physical machine. This technology has revolutionized the way businesses operate by enabling them to maximize hardware usage, reduce costs, and improve disaster recovery processes.
Architecture
The architecture of Hyper-V comprises several components, including the hypervisor, virtual machines, and virtual networks. Hyper-V features a Type 1 hypervisor-based architecture. The hypervisor virtualizes processors and memory. It provides mechanisms for the virtualization stack in the root partition to manage child partitions, virtual machines (VMs) and expose services such as I/O (input/output) devices to the VMs.
The root partition owns and has direct access to the physical I/O devices. The virtualization stack in the root partition provides a memory manager for VMs, management APIs, and virtualized I/O devices. It also implements emulated devices, such as the integrated device electronics (IDE) disk controller and PS/2 input device port. And it supports Hyper V-specific synthetic devices for increased performance and reduced overhead.
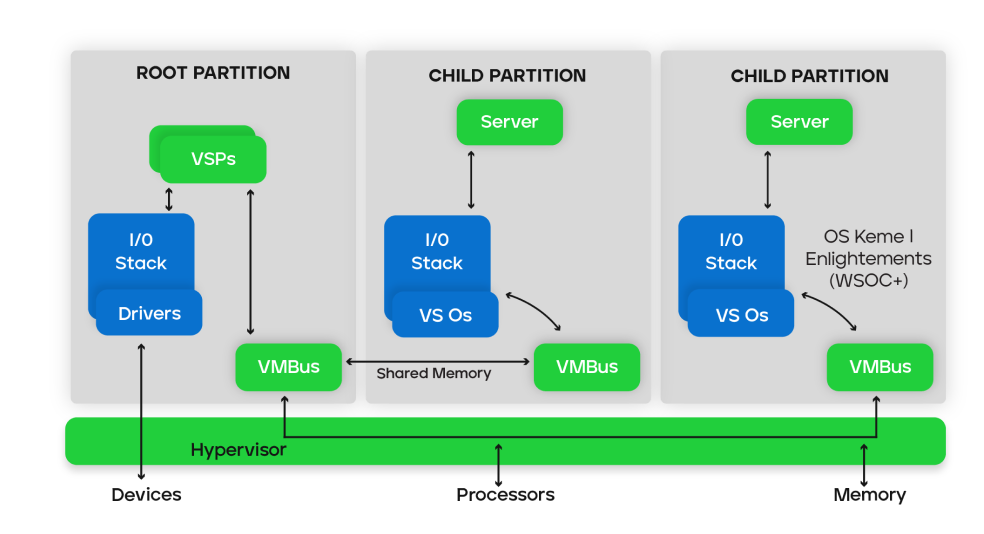
The Hyper-V-specific I/O architecture consists of virtualization service providers (VSPs) in the root partition and virtualization service clients (VSCs) in the child partition. Each service is exposed as a device over VM Bus, which acts as an I/O bus and enables high-performance communication between VMs that use mechanisms such as shared memory. The guest operating system’s Plug and Play manager enumerates these devices, including VM Bus, and loads the appropriate device drivers, virtual service clients. Services other than I/O are also exposed through this architecture.
- Hypervisor
The hypervisor is the core component of Hyper-V. It’s responsible for creating, running, and managing VMs. The hypervisor operates directly on the hardware, allowing for improved performance and efficiency. It’s designed to ensure that each VM operates independently, without interference from other VMs on the same host. This isolation is crucial for maintaining the security and stability of each VM.
- Virtual Machines
Virtual machines are software emulations of physical computers. They run their own operating systems and applications, just like a physical computer. Hyper-V supports the creation of both Generation 1 and Generation 2 VMs, each with its own set of capabilities and limitations. Generation 1 VMs support legacy hardware and are compatible with most operating systems. On the other hand, Generation 2 VMs support modern features such as Secure Boot and larger boot volumes but are only compatible with certain versions of Windows and Linux.
- Virtual Networks
Virtual networks in Hyper-V allow VMs to communicate with each other and with the outside world. They can be configured in various ways to suit different networking requirements. For example, you can create private networks for VMs that don’t require external connectivity, internal networks for communication between VMs and the host, or external networks for connecting VMs to the physical network.
Key Benefits of Hyper-V
Hyper-V comes with a host of features that enhance its functionality and usability. These features are designed to improve the performance, scalability, and manageability of virtual environments.
1. Live Migration
Live Migration is a feature that allows you to move running VMs from one Hyper-V host to another without any downtime. This is particularly useful for performing maintenance tasks without disrupting services. Live Migration works by transferring the VM’s memory and state from the source host to the destination host while the VM continues to run. Once the transfer is complete, the VM is switched over to the destination host, and the user experiences no noticeable downtime.
2. High Availability
Hyper-V, when used in conjunction with other Microsoft technologies like Failover Clustering, can provide high availability for your VMs. This ensures that your services remain available even in the event of a host failure. Failover Clustering works by grouping multiple Hyper-V hosts into a cluster. If one host fails, the VMs on that host are automatically moved to another host in the cluster, minimizing downtime.
3. Extensible Switch
The Hyper-V extensible switch is a virtual network switch that you can extend and customize to suit your networking needs. It supports a variety of third-party extensions, allowing for greater flexibility and control. With the extensible switch, you can implement advanced networking features such as intrusion detection, traffic shaping, and network isolation directly on the virtual switch.
4. Development and test
Duplicate VM or Reproduce different computing environments for Testing or Development with the readily available resources in any Hyper-V enabled Server or Desktop.


